🚀 Kindle Countdown Deal on “A Guide to Citizen Development in Microsoft 365 with Power Platform” 🚀
Are you ready to revolutionize the way you work with Microsoft 365? This comprehensive guide is a must-read for professionals, educators, students, and anyone keen to maximize Microsoft’s powerful tools in a modern, hybrid workspace.
🌟 Get a Free Sneak Peek and Discover the World of Citizen Development!
Don’t miss out - access the book directly here! Get Your Copy Today! and start transforming the way you work with Microsoft 365.
🔥 **Kindle Countdown Deal is live, ** Grab your copy and dive deep into #microsoft365 and #powerplatform, unlocking the potential of Citizen Development. Share your thoughts and reviews on Amazon Kindle after reading!
Key Highlights of the Book:
- Democratizing App Development: Understand the transformative role of Citizen Development in Microsoft 365.
- For a Diverse Audience: Tailored for IT specialists, cloud service administrators, business architects, and beginners.
- From Basics to Advanced: A comprehensive range covering foundational knowledge to advanced topics.
- Deep Dive into Microsoft 365: Explore features, applications, and nuances of Microsoft 365 and associated products.
- Real-World Applications: Filled with practical scenarios for workplace efficiency.
🌐 Embark on Your Transformative Journey Today with the Kindle Countdown Deal!
Why Read This Book?
- Empower Yourself and Your Team: Master Microsoft 365 apps and tools.
- Stay Ahead in Digital Transformation: Understand Microsoft 365’s role across sectors.
- Enhance Productivity and Well-being: Discover how Microsoft 365 improves employee experiences.
📘 About the Book: The book offers a guide to harnessing Microsoft 365’s capabilities for various audiences. It covers the Microsoft 365 ecosystem, cloud computing, Microsoft 365 services, apps, Power Fx, Adaptive Cards, Power Apps, and Dataverse, along with security, compliance, and licensing. It also introduces AI and Generative AI components of the Power Platform.
📚 Read and Reimagine the World Around You with “A Guide to Citizen Development in Microsoft 365 with Power Platform”! 📚
This book covers:
-
Introduction to Microsoft 365 Ecosystem: Provides insights into the Microsoft Cloud ecosystem, including Microsoft 365, Microsoft Teams, and the Power Platform.
-
Cloud Computing and Citizen Development: Offers a succinct explanation of cloud computing, cloud services, deployment strategies, and the role of citizen development in bridging digital transformation gaps.
-
Microsoft 365 Services Overview: Delves into the diverse services of Microsoft 365, such as SharePoint, OneDrive, and Teams, guiding readers on enhancing productivity and collaboration.
-
Microsoft 365 Apps: Introduces design thinking, utilization of whiteboard templates, and productivity tools like Forms, Sway, Bookings, OneNote, and Planner.
-
Power Fx Introduction: Learn Excel-style low-code programming with Power Fx and understand its usage in Power Apps, Dataverse, and Power Automate.
-
Adaptive Cards: Learn about different categories of cards, their integration with Microsoft Graph, and their application within Teams.
-
Power Apps and Dataverse: Understand canvas and model-driven apps, and explore the functionalities and limitations of Dataverse for Teams.
-
Security, Compliance, and Licensing: Gain foundational knowledge on Cloud Security 101, role-based security within Microsoft 365, shared responsibility, data sovereignty, and Microsoft 365 plans comparison.
-
AI Builder on Power Platform: Dive into prebuilt AI models and their practical applications for the Power Platform.
-
Generative AI and LLM-based Apps: Understand the nuances of Generative AI and LLMs, and explore third-party Power Platform connectors and emerging AI trends in citizen development.
This book guides professionals, students, and educators aiming to leverage Microsoft 365 for real-time hybrid workspaces and collaborative scenarios. It covers various topics from foundational to advanced, ensuring readers are equipped with the necessary skills and knowledge to use Microsoft 365 products and features proficiently.
The book delves into the software development ecosystem, highlighting Microsoft 365’s Citizen development as an alternative low-code and no-code solution using Microsoft Teams and Power Platform. It provides a basic understanding of cloud computing and the role of Citizen Development, emphasizing its value in offering short-term IT solutions without replacing traditional IT. The reader is introduced to various Microsoft 365 services, including SharePoint, Exchange, OneDrive, and Microsoft Teams.
The book explores the collaborative features of SharePoint Online and OneDrive and delves into the low-code language Power Fx, Adaptive Cards, Power Apps, Power Automate, Power Pages, and Microsoft Dataverse while excluding topics on Power BI and Power Virtual Agents in this first edition. Security, compliance, and licensing within Microsoft 365 are addressed from a Citizen Development viewpoint, albeit not in-depth. The book further introduces AI and Generative AI components of the Power Platform. Through Jane’s experiences, a persona, readers gain insights into challenges faced during Microsoft 365 adoption, focusing on Citizen Development.
Also, targeted at IT admins and developers new to Microsoft 365, the book showcases practical scenarios for enhancing tech-savvy work efficiency and productivity but is not intended for advanced professionals already well-versed in the platform.
Book outline - A Guide to Citizen Development in Microsoft 365 with Power Platform
Democratizing App Development: The Microsoft 365 Way Citizen developers, IT specialists, cloud service administrators, and business architects have shown keen interest in Citizen development, the deployment, and utilization of Microsoft 365 apps. This is especially true when considering the Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) and Low-code No-code (LCNC) offerings from Microsoft Cloud. This book is crafted for professionals, students, and educators across schools, colleges, and universities who have prior experience with Microsoft Office, Windows 10/11, and devices like PCs, laptops, or Macs. While some chapters cater to advanced professionals, the content remains beneficial for a wider readership. The book spans from introductory to advanced topics, with clear demarcations for each level.
Readers will gain insights into leveraging Microsoft 365 for real-time hybrid workspaces and collaborative scenarios. The book elucidates the inherent features, applications, and nuances of Microsoft 365 and associated products. It also sheds light on the low-code no-code platforms and citizen development within the Microsoft 365, Microsoft Teams, and Microsoft Power Platform ecosystem.
The content provides foundational knowledge on Cloud Computing 101 and Cloud Security 101, acquainting readers with the basics of Citizen development and certain administrative facets of Microsoft 365, Teams, Security, compliance, and licensing.
Advanced topics, such as designing solutions on the Power Platform products like Power Fx, Power Apps, Power Automate, Power Virtual Agents, Power BI, AI Builder, and Generative AI, are also covered. Additionally, the book touches upon Microsoft 365 Defender, and Microsoft Entra, while intentionally excluding products like Stream, Yammer, Microsoft Search, Microsoft Purview, and Microsoft Dynamics 365.
Developers will find value in exploring the Microsoft Team development toolkit and crafting custom connectors on Microsoft Teams for solutions not available as standard features.
From foundational 101 topics to advanced concepts, this book equips readers with the skills to proficiently use Microsoft 365 apps, development tools, administration, and security features. It aims to enhance workplace efficiency and extends knowledge beyond traditional Windows and Office in a contemporary hybrid workspace.
In 2018, industry giants Adobe, Microsoft, and SAP unveiled open data initiatives to craft digital experiences centered around Adobe Experience Cloud, Microsoft Dynamics, Office 365 (now Microsoft 365), and SAP C/4HANA. The Common Data Model was introduced to standardize data formats. As part of this initiative, Microsoft developed the Microsoft Dataverse, with specific details on the Dataverse for Teams environment covered in Chapter 06.
The Microsoft 365 Platform stands as a pillar for digital transformation, enhancing employee experiences, productivity, and well-being across sectors like Education, Manufacturing, Government, and more, catering to businesses of all sizes.
About the first edition of this book
The book delves into the software development ecosystem, highlighting Microsoft 365’s Citizen development as an alternative low-code and no-code solution using Microsoft Teams and Power Platform. It provides a basic understanding of cloud computing and the role of Citizen Development, emphasizing its value in offering short-term IT solutions without replacing traditional IT. The reader is introduced to various Microsoft 365 services including SharePoint, Exchange, OneDrive, and Teams.
The book explores the collaborative features of SharePoint Online and OneDrive and delves into the low-code language Power Fx, Adaptive Cards, Power Apps, Power Automate, Power Pages, and Microsoft Dataverse, while excluding topics on Power BI and Power Virtual Agents in this first edition. Security, compliance, and licensing within Microsoft 365 are addressed from a Citizen Development viewpoint, albeit not in-depth. The book further introduces AI and Generative AI components of the Power Platform. Through Jane’s experiences, readers gain insights into challenges faced during Microsoft 365 adoption, with a focus on Citizen Development. Targeted at IT admins and developers new to Microsoft 365, the book showcases practical scenarios for enhancing tech-savvy work efficiency and productivity but is not intended for advanced professionals already well-versed in the platform.

Let’s embark on this transformative journey together!
The book portrays Jane Doe, a lecturer at Newland University, who is delving into the use of Digital Technology in Education. Tasked with overseeing an Online Postgraduate program, she is responsible for onboarding a diverse group of 150 students from around the globe. Her immediate responsibilities include recruiting student buddies, evaluating students’ dissertation topics, assigning mentors, and establishing a student support cell. Additionally, she must conduct an introductory session. To assist with these duties, she approached the university’s IT department. In response, they provided her with Microsoft 365 and a collection of articles on its usage. However, she feels overwhelmed by the influx of information. Jane Doe serves as the Program Director for this online postgraduate course. The program’s success hinges on her leadership, and her experiences will form the foundation of her thesis on the application of Digital Technology in Education. This book aims to guide Jane Doe, along with other IT department members and a Pro Developer, in effectively utilizing Microsoft 365 and Teams to enhance her work at the university.
Book Outline
Introductory Chapter 01 - Unleashing the Potential of Citizen Development in Microsoft 365
This chapter provides an introduction to Microsoft 365, Microsoft Teams, and the Power Platform, offering insights into the Microsoft Cloud ecosystem.
In the first chapter of “Citizen Development in Microsoft 365,” the author delves into the intricacies of Microsoft 365, Microsoft Teams, and the Microsoft Power Platform. The chapter emphasizes the significance of Rapid Application Development (RAD) and contrasts it with custom-built software solutions. It highlights the potential of Low-code and No-code (LCNC) development approaches in creating short-term solutions that can evolve into long-term ones. The chapter aims to familiarize readers with various concepts around RAD, Citizen development, and how to harness the Microsoft Cloud for crafting compelling business scenarios. It also provides an overview of Microsoft 365, Microsoft Teams, and the Power Platform, guiding readers on getting started with a Microsoft work account, Multi-Factor Authentication MFA, and various apps. The chapter underscores the importance of digital transformation and the pivotal role Microsoft 365 plays in such transformational efforts.
The digital age has ushered in a new era of software development, where the emphasis is not just on coding but also on accessibility and democratization. Central to this shift is the rise of Low-code and No-code (LCNC) platforms, as highlighted in the chapter. These innovative platforms are transforming the way applications are built, making it possible for individuals without deep coding expertise to design and deploy powerful solutions. By simplifying the development process, LCNC platforms are breaking down barriers, allowing a broader range of individuals to participate in the creation of digital tools. This not only accelerates the pace of innovation but also fosters a more inclusive environment where IT professionals collaborate seamlessly with business users. The result is a more agile, responsive, and diverse software ecosystem that caters to the evolving needs of modern businesses.
Microsoft’s vision for the future is deeply rooted in the belief that technology should be an enabler, accessible and beneficial to everyone, regardless of their technical expertise. This ethos is clearly reflected in their strategic investments in platforms such as Microsoft 365, Microsoft Teams, and the Power Platform. These tools are not just standalone products; they represent a cohesive ecosystem that integrates seamlessly, offering users a range of capabilities from collaboration to automation. By democratizing AI and other advanced technologies, Microsoft is ensuring that businesses, educators, and individuals can harness the power of AI to solve real-world challenges, enhance productivity, and drive innovation. This approach not only positions Microsoft as a leader in the tech industry but also underscores its commitment to fostering a culture where technology amplifies human potential, creativity, and collaboration.
The modern workplace is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by technological advancements and shifts in societal expectations. The chapter highlights this evolution, emphasizing the increasing adoption of hybrid work models where employees split their time between traditional office settings and remote locations. This new paradigm presents both opportunities and challenges, necessitating tools and solutions that support flexibility while maintaining productivity and collaboration. Microsoft, with its forward-thinking approach, has introduced solutions like Microsoft Viva, specifically tailored to address the nuances of the hybrid workplace. Viva integrates various modules, from employee well-being to knowledge sharing, ensuring that teams remain connected, engaged, and informed, irrespective of where they work. By providing such holistic solutions, Microsoft is not only responding to the immediate needs of businesses but also shaping the future of work, championing an environment that prioritizes both efficiency and employee well-being.
In conclusion, the chapter offers a exploration of the evolving landscape of modern workplaces, emphasizing the pivotal role of technology in shaping this transformation. As hybrid work models emerge as the new standard, the need for adaptive and integrative solutions becomes paramount. Microsoft, recognizing these shifts, has proactively developed tools like Microsoft Viva to address the multifaceted challenges and opportunities presented by the hybrid work paradigm. By democratizing AI and fostering a culture of innovation, Microsoft is not only meeting the immediate demands of businesses but also laying the foundation for a future where technology and human potential harmoniously coalesce. This chapter serves as a testament to the importance of adaptability, foresight, and innovation in navigating the ever-changing dynamics of the workplace.
Chapter 02 Unveiling the Power of Cloud Computing 101 and Citizen Development
This chapter succinctly explains cloud computing, cloud services, deployment strategies, and citizen development.
The chapter 02 on Cloud Computing 101 and Citizen Development delves into the transformative world of cloud computing, emphasizing its profound impact on our daily lives and work processes. The chapter highlights how cloud services have made tasks more efficient, from recording life moments to enabling remote work and breaking language barriers. The global shift in communication, work, and life dynamics is attributed to the advancements in cloud technology. This chapter provides a understanding of cloud computing, discussing its fundamental concepts, service models, and the principles of well-architected frameworks. It also explores the software development ecosystem, particularly the rise of citizen development and the expanding Low-code/No-code platform market. The objectives of the chapter are to familiarize readers with cloud concepts essential for recognizing the benefits and ROI of using cloud platforms. Topics covered include cloud computing basics, cloud concepts, cloud service models, well-architected frameworks, software development ecosystems, citizen development, and the Low-code/No-code platform market.
The evolution of cloud computing has ushered in a new era of communication and work dynamics, reshaping how businesses and individuals operate. This chapter delves deep into the transformative power of cloud technology, highlighting its profound impact on global communication patterns and work methodologies. As organizations and individuals increasingly rely on cloud services for a myriad of tasks, from data storage to real-time collaboration, the traditional boundaries of workplaces are being redefined. The chapter emphasizes that these shifts are not mere trends but are indicative of a larger paradigm shift in the way we perceive and engage with technology. The advancements in cloud computing are not just enhancing efficiency but are also democratizing access, ensuring that cutting-edge technological solutions are within reach for everyone, regardless of their technical expertise.
The rise of Low-code/No-code (LCNC) platforms marks a significant shift in the software development landscape. These platforms are democratizing the application development process, allowing individuals, even those without a technical background, to create functional and sophisticated applications. This empowerment stems from the platform’s intuitive design, drag-and-drop interfaces, and pre-built templates, which simplify the traditionally complex coding processes. As a result, businesses can rapidly prototype, test, and deploy solutions, accelerating digital transformation and fostering innovation. Moreover, by harnessing the capabilities of LCNC platforms, organizations can bridge the gap between IT departments and other business units, promoting collaboration and ensuring that solutions are tailored to specific needs. In essence, the growth of LCNC platforms is reshaping the narrative of software development, emphasizing inclusivity, agility, and user-centric design.
The financial dynamics of cloud computing present a transformative approach to how organizations allocate and manage their IT budgets. The chapter delves into the economic considerations of adopting cloud services, particularly highlighting the distinction between Capital Expenditure (CapEx) and Operating Expenditure (OpEx). Traditionally, IT infrastructure investments were largely CapEx-oriented, requiring significant upfront costs for hardware, software, and related assets. However, with the advent of cloud computing, there’s a paradigm shift towards OpEx, where organizations essentially “rent” services and pay based on usage. This model offers flexibility, scalability, and eliminates the need for hefty initial investments. In the cloud context, OpEx allows businesses to adapt quickly to changing needs, only paying for the resources they consume. By understanding the financial implications of CapEx versus OpEx in the realm of cloud services, organizations can make informed decisions, optimize costs, and achieve greater financial agility. This economic perspective is crucial for businesses to harness the full potential of cloud computing while ensuring fiscal responsibility and sustainability.
In conclusion, The chapter 02 on Cloud Computing 101 and Citizen Development of “Citizen Development in Microsoft 365” offers a exploration into the transformative world of cloud computing and its profound implications on modern work and communication dynamics. By delving into the intricacies of cloud services, from its foundational concepts to the economic considerations of CapEx and OpEx, the chapter provides readers with a holistic understanding of the cloud landscape. Furthermore, the emphasis on the rise of Low-code/No-code platforms underscores the democratization of software development, highlighting a future where application creation is accessible to all, irrespective of technical expertise. The chapter serves as a testament to the evolving nature of technology and its potential to reshape industries, redefine roles, and drive innovation in an ever-connected world.
Chapter 03 on Microsoft 365 Services - Unlocking Productivity: Your Guide to Microsoft 365 Services

This chapter provides an overview of the diverse services offered by Microsoft 365, including SharePoint, OneDrive, and Teams. It guides readers on initiating these services to enhance daily work productivity and foster collaboration using these tools. The chapter also delves into the functionalities of Microsoft Teams, covering aspects like chat, teams, channels, connectors, and apps. The chapter 03 Microsoft 365 Services Overview provides a overview of Microsoft 365 services, emphasizing SharePoint, Exchange, OneDrive for Business, and Microsoft Teams. The chapter introduces Jane Doe, a lecturer at Newland University, who is leading an online postgraduate program. Jane aims to integrate Digital Technology in Education and will utilize Microsoft 365 to enhance the educational experience. The chapter delves into the various features of Microsoft Teams, such as chat, teams, channels, connectors, and apps. It further distinguishes between Microsoft 365’s Products, Services, and Apps. The chapter also touches upon SharePoint Online, emphasizing its value in content management systems and its integration with Microsoft 365, Microsoft Teams, and OneDrive. The chapter concludes by discussing the SharePoint admin center and the versatility of the SharePoint site for content sharing and collaboration.
Educators like Jane Doe can leverage Microsoft 365 in numerous ways to revolutionize the educational experience for students: Collaborative Learning with Microsoft Teams: Jane can create a virtual classroom using Microsoft Teams, where students can attend live lectures, participate in discussions, and collaborate on group projects in real-time. The platform also allows for breakout rooms, facilitating smaller group discussions or tutoring sessions. Interactive Presentations with PowerPoint: Using PowerPoint’s advanced features, Jane can create interactive presentations, incorporating quizzes, polls, and multimedia elements to engage students and test their understanding.
Organized Curriculum with OneNote: Jane can use OneNote Class Notebook to organize lesson plans, distribute assignments, and provide a space for students to take notes, all in a digital format.
Seamless Document Sharing with SharePoint and OneDrive: Jane can share reading materials, assignments, and resources with students using SharePoint or OneDrive, ensuring that everyone has access to the necessary materials. Students can also submit their assignments through these platforms.
Engaging Virtual Lessons with Whiteboard: The Microsoft Whiteboard app can be used during virtual lessons to draw diagrams, illustrate concepts, and encourage students to participate in brainstorming sessions.
Feedback and Grading with Microsoft Forms and Excel: Jane can use Microsoft Forms to create quizzes and surveys to gauge student understanding. The results can be automatically populated into Excel, where she can analyze the data, track student progress, and provide personalized feedback.
Accessibility Features: Microsoft 365 comes with built-in accessibility features like Immersive Reader in Word and OneNote, which can read text aloud, break it into syllables, and increase spacing. This ensures that all students, including those with learning disabilities, can access the content.
Continuous Learning with Stream: Jane can record her lectures and upload them to Microsoft Stream, allowing students to revisit lessons at their own pace or catch up if they missed a session. Secure Communication with Outlook: Jane can maintain open lines of communication with students and parents using Outlook, ensuring privacy and security in all correspondence.
Integration with Third-Party Educational Apps: Microsoft 365 integrates seamlessly with various educational apps and platforms, allowing Jane to incorporate diverse tools into her teaching methodology.
By harnessing the power of Microsoft 365, educators like Jane Doe can create a dynamic, interactive, and inclusive learning environment that caters to the diverse needs of modern students. Organizations aiming to maximize the potential of Microsoft 365 for their specific needs can adopt the following strategies:
-
Needs Assessment: Begin with a thorough assessment of the organization’s needs. Identify the challenges faced by different departments and determine how Microsoft 365’s suite of tools can address them.
- Tailored Training: Offer customized training sessions for employees based on their roles. For instance, marketing teams might benefit more from in-depth training on Power BI, while HR might focus on Microsoft Teams for communication.
- Leverage SharePoint for Collaboration: Use SharePoint to create intranet sites for different departments, ensuring that all team members have access to relevant documents, calendars, and other resources.
- Adopt Microsoft Teams for Communication: Encourage teams to use Microsoft Teams for meetings, chats, and collaboration. This ensures seamless communication, especially for remote or hybrid teams.
- Data Analysis with Power BI: Integrate Power BI to analyze data and derive actionable insights. This can be crucial for departments like sales, marketing, and finance.
- Automate Workflows with Power Automate: Streamline repetitive tasks using Power Automate. By automating workflows, organizations can enhance efficiency and reduce manual errors.
- Stay Updated: Microsoft frequently updates its suite with new features and improvements. Regularly check for updates and inform employees about new functionalities that can benefit their tasks.
- Feedback Loop: Establish a feedback mechanism where employees can share their experiences, challenges, and suggestions related to Microsoft 365 products. This can help in identifying areas of improvement.
- Security Protocols: Utilize Microsoft 365’s advanced security features to protect sensitive data. Ensure that employees are trained on best practices for data security.
- Integration with Third-Party Tools: Microsoft 365 can be integrated with a plethora of third-party tools. Identify which external tools are crucial for your organization and integrate them for a unified experience.
- Regular Audits: Periodically review how different teams are using Microsoft 365. This can help in identifying underutilized tools and potential areas for further training.
- Engage with Microsoft Support and Communities: Leverage the vast community of Microsoft 365 users and official support channels to address challenges, learn best practices, and discover innovative ways to use the platform.
By adopting a strategic, proactive, and user-centric approach, organizations can ensure they harness the full spectrum of capabilities offered by Microsoft 365, tailored to their unique operational needs.
SharePoint Online, with its robust content management and collaboration capabilities, offers businesses a versatile platform to foster a collaborative work environment. Here’s how businesses can effectively harness its potential:
- Centralized Document Repository: Use SharePoint Online to create a centralized location for all company documents, ensuring that employees can easily access, share, and collaborate on documents in real-time.
- Team Sites: Create dedicated sites for different departments or project teams. These sites can house all relevant documents, calendars, task lists, and other resources specific to that team.
- Version Control: SharePoint Online automatically tracks changes made to documents, allowing for version history viewing and restoring previous versions if needed. This ensures that teams can collaborate without fear of losing work.
- Integrated Communication Tools: Integrate SharePoint with Microsoft Teams or Yammer to facilitate discussions, meetings, and chats directly within the platform, ensuring seamless communication.
- Workflow Automation with Power Automate: Automate routine processes, such as document approvals or content updates, using Power Automate. This streamlines operations and ensures consistency.
- Customizable Dashboards: Use SharePoint’s dashboard capabilities to create visual representations of project statuses, key performance indicators, or other essential metrics, ensuring that teams are always informed.
- External Collaboration: SharePoint Online allows for secure sharing with external stakeholders, such as clients or partners. This ensures that collaboration isn’t limited just to internal teams.
- Mobile Accessibility: With SharePoint’s mobile apps, employees can access content and collaborate on the go, ensuring continuity and flexibility.
- Granular Permission Settings: Control who can view, edit, or share content with SharePoint’s detailed permission settings. This ensures data security while still promoting collaboration.
- Integration with Other Microsoft 365 products: SharePoint Online integrates seamlessly with tools like OneDrive, Microsoft Lists, and more. This interconnected ecosystem further enhances collaboration capabilities.
- Custom Apps and Solutions: Utilize the SharePoint Framework (SPFx) to develop custom apps or web parts tailored to specific business needs, ensuring that the platform aligns perfectly with organizational workflows.
- Feedback and Surveys: Use SharePoint to create feedback forms or surveys, gathering insights from employees to continuously improve collaboration strategies.
- Knowledge Base and Wikis: Establish a knowledge base or wiki within SharePoint to document best practices, guidelines, or FAQs, ensuring that employees have a go-to resource for common queries.
By strategically implementing these features and practices, businesses can transform SharePoint Online into a powerful hub for collaboration, ensuring that teams work cohesively, efficiently, and innovatively.
In wrapping up the chapter 03 on Microsoft 365 Services Overview of “Citizen Development in Microsoft 365,” it’s evident that Microsoft 365’s suite of tools and services, particularly SharePoint Online, offers unparalleled opportunities for businesses to foster collaboration and streamline operations. The chapter provides a deep dive into the multifaceted capabilities of these tools, from content management to real-time communication, all tailored to meet the evolving needs of modern workplaces. By introducing practical scenarios, such as Jane Doe’s endeavors at Newland University, the chapter underscores the real-world applicability and transformative potential of Microsoft 365. As organizations navigate the digital landscape, tools like SharePoint Online emerge not just as software solutions but as catalysts for change, driving innovation, efficiency, and collaboration. The insights provided in this chapter serve as a roadmap for businesses, guiding them towards a future where technology and human collaboration coalesce seamlessly.
Chapter 04 on Microsoft 365 Apps - Elevate Efficiency: Microsoft 365 Apps at Your Fingertips
Grasp the concept of design thinking and learn how to utilize whiteboard templates for brainstorming techniques such as the affinity diagram, and problem-solving tools like the cause-and-effect diagram. Dive into cost/benefit evaluations, assumption grids, gap/feasibility analyses, and design and research templates like empathy maps, feedback grids, the kano model, storyboarding, and user interviews. Additionally, explore more templates focused on strategy, project planning, workshops, and learning. Enhance your workplace productivity using tools like Forms, Sway, Bookings, OneNote, and Planner.
The chapter 04 on Microsoft 365 Apps of “Citizen Development in Microsoft 365” delves deep into the world of Microsoft 365 Apps. The chapter introduces the apps model, design thinking, and the utilization of whiteboard templates for brainstorming. It emphasizes the significance of tools like Forms and Sway in enhancing workplace productivity. The chapter also explores the concept of design thinking, highlighting its importance in understanding user needs and iterating solutions for optimal outcomes. Microsoft Loop is introduced as a tool that fosters real-time collaboration, making team interactions feel organic and straightforward. The chapter also touches upon the challenges of digital overload in the modern hybrid workplace and offers insights and strategies to combat these challenges, ensuring a balanced and productive work environment.
Three Key Insights from the Chapter:
- The Power of Microsoft 365 Apps: The chapter underscores the versatility of Microsoft 365 Apps, emphasizing their role in streamlining knowledge discovery, content organization, and collaboration. With tools like Microsoft Loop, Whiteboard, Forms, and Sway, users are equipped to enhance their digital endeavors and foster a collaborative work environment.
- Embracing Design Thinking: Microsoft 365 integrates design thinking principles to boost user experiences. By understanding user needs, defining problems, and creating solutions through iterative testing, Microsoft ensures its products are user-centric, functional, and intuitive. Tools like Microsoft Loop exemplify this commitment, enabling real-time collaboration and co-creation.
- Addressing Digital Overload: The modern hybrid workplace presents challenges like excessive meetings, unscheduled communications, and navigating different time zones. The chapter offers strategies and best practices, emphasizing the importance of setting boundaries, using collaboration tools effectively, and adopting a user-centric approach to ensure a harmonious work environment.
Organizations are increasingly recognizing the value of data in driving decision-making, innovation, and competitive advantage. Microsoft 365 Apps play a pivotal role in helping organizations harness the power of this “new oil.” Here’s how:
- Integrated Data Analytics: Tools like Microsoft Excel have evolved beyond simple spreadsheets. With Power Query and Power Pivot, users can pull data from various sources, transform it, and create complex data models. Power BI, integrated with Microsoft 365, allows for the visualization and sharing of these insights across the organization.
- Collaboration and Real-time Sharing: Microsoft Teams and SharePoint facilitate real-time data sharing and collaboration. Teams can work on documents simultaneously, ensuring that everyone has access to the latest data and insights.
- Secure Data Storage and Compliance: OneDrive and SharePoint provide secure cloud storage solutions, ensuring that data is not only accessible but also protected. Microsoft 365’s advanced security features and compliance tools ensure that data is handled according to industry regulations.
- Automation and Workflow Integration: Power Automate allows organizations to create automated workflows between apps and services. This helps in streamlining data collection, processing, and dissemination.
- Custom App Development: With Power Apps, organizations can create custom apps tailored to their needs without extensive coding. These apps can pull data from various sources within the Microsoft 365 ecosystem, providing tailored insights.
- Knowledge Mining: Project Cortex, part of Microsoft 365, uses AI to mine documents and other data, turning them into shared knowledge across the organization.
- Seamless Integration: Microsoft 365 Apps are designed to work seamlessly together, ensuring that data can flow effortlessly between apps like Outlook, Planner, and To-Do, keeping teams aligned and informed
In essence, Microsoft 365 Apps provide a ecosystem that allows organizations to collect, analyze, share, and act upon data effectively, ensuring they remain agile and informed in a rapidly changing business environment.
The integration of design thinking principles in Microsoft 365 Apps has been instrumental in enhancing user experiences and boosting productivity. Here’s how:
- Empathy for Users: Design thinking starts with understanding the user’s needs, challenges, and pain points. Microsoft 365 Apps are developed with a deep understanding of the diverse needs of users, ensuring that the tools are intuitive, user-friendly, and address real-world challenges.
- Iterative Development: Design thinking emphasizes prototyping and iterative testing. Microsoft frequently releases updates and new features for its 365 Apps based on user feedback and testing, ensuring that the tools evolve to meet changing user needs.
- Holistic Solutions: Instead of focusing on isolated features, design thinking looks at the entire user journey. Microsoft 365 Apps are integrated seamlessly, allowing users to transition effortlessly between tasks and tools, enhancing the overall workflow.
- Collaboration-Centric Design: Recognizing the importance of collaboration in modern workplaces, Microsoft 365 Apps like Teams, SharePoint, and OneDrive are designed to facilitate easy sharing, communication, and joint work, fostering a collaborative environment.
- Flexibility and Customization: Design thinking values solutions that are adaptable to individual needs. Microsoft 365 Apps offer a high degree of customization, allowing organizations to tailor the tools to their specific requirements.
- Problem-Solving Approach: Design thinking is all about solving problems. Microsoft 365 Apps are designed not just as software tools but as solutions to workplace challenges, be it communication barriers, data management issues, or workflow inefficiencies.
- Inclusivity and Accessibility: Design thinking emphasizes designing for all users. Microsoft 365 Apps come with a range of accessibility features, ensuring that they cater to users with diverse abilities and needs.
- Continuous Learning and Improvement: Design thinking promotes a culture of continuous learning. Microsoft offers extensive training resources, tutorials, and support for its 365 Apps, ensuring that users can continuously learn and make the most of the tools.
In conclusion, the integration of design thinking principles ensures that Microsoft 365 Apps are not just functional but also user-centric, intuitive, and tailored to address the challenges and needs of modern workplaces. This focus on the user experience and holistic problem-solving directly contributes to improved productivity and user satisfaction.
As the modern workplace undergoes rapid transformation, digital overload has emerged as a significant challenge. Microsoft 365 offers a suite of tools that can help organizations address this issue and prioritize employee well-being:
- Focused Collaboration with Microsoft Teams: Microsoft Teams centralizes communication, reducing the need to juggle multiple platforms. Features like “Do Not Disturb” and “Quiet Hours” allow employees to set boundaries and minimize distractions.
- Prioritization with Microsoft To Do: This tool helps employees organize tasks, set priorities, and manage their workload effectively, reducing feelings of overwhelm.
- Mindful Breaks with Microsoft Viva Insights: Viva Insights offers personalized recommendations to take mindful breaks, focus on important tasks, and even schedule “focus time” to work without interruptions.
- Streamlined Workflows with Power Automate: By automating repetitive tasks, Power Automate reduces manual workload, allowing employees to focus on more meaningful work.
- Knowledge Management with Project Cortex: Instead of spending time searching for information, Project Cortex uses AI to organize content and expertise across the organization, making it easier for employees to find what they need.
- Flexible Work Schedules: Microsoft 365’s calendar and scheduling tools enable flexible work arrangements, allowing employees to balance work with personal commitments and reduce burnout.
- Training and Skill Development with Microsoft Learn: Continuous learning opportunities can help employees feel more competent and less overwhelmed by new technologies or processes.
- Secure and Controlled Data Access: Tools like OneDrive and SharePoint ensure that employees have access to the data they need without being overwhelmed by unnecessary information. Advanced security features also reduce the stress associated with potential data breaches.
- Feedback Mechanisms with Microsoft Forms: Regular feedback can help organizations identify areas of digital overload and address them proactively.
- Digital Detox Initiatives: Using the analytics and insights from Microsoft 365 products, organizations can encourage digital detox periods, ensuring employees take breaks from screen time.
- Accessibility Features: Microsoft 365 comes equipped with features that cater to diverse needs, ensuring that all employees can work comfortably and efficiently.
- Integration and Simplification: Microsoft 365’s integrated ecosystem means fewer standalone tools and platforms, leading to a more streamlined digital experience.
In essence, while the digital transformation of the workplace offers numerous advantages, it also presents challenges. By leveraging Microsoft 365 products thoughtfully and proactively, organizations can mitigate the risks of digital overload, fostering a work environment that prioritizes efficiency, collaboration, and, most importantly, employee well-being.
The chapter 04 on Microsoft 365 Apps of “Citizen Development in Microsoft 365” delves deep into the expansive realm of Microsoft 365 Apps, emphasizing their transformative potential in today’s digital age. The chapter introduces the apps model, the principles of design thinking, and the challenges of digital overload. It underscores the significance of data in the modern era, likening it to “the new oil” and highlighting how Microsoft 365 acts as a conduit, making this data securely accessible to knowledge workers. The chapter also explores the extensibility of Microsoft 365, the power of the Microsoft Graph API, and the integration capabilities of Microsoft Teams. Furthermore, it touches upon the principles of design thinking, emphasizing empathy, iteration, and user-centricity. The chapter concludes by addressing the challenges of digital overload in the modern hybrid workplace, offering insights and strategies to combat these challenges and foster a more harmonious and productive work environment. The insights provided in this chapter are invaluable for organizations and individuals aiming to harness the full potential of Microsoft 365 Apps in their digital endeavors.
Chapter 05 - SharePoint Online and OneDrive - Collaborate and Thrive:

Harnessing SharePoint Online and OneDrive for Success Utilize SharePoint sites, including Teams and communication sites, to craft business scenarios centered on Microsoft Lists. Organize storage content and share files securely using OneDrive for Business. Learn the smooth transition between personal and business accounts, grasp the principles of Information Rights Management (IRM), and understand the constraints and limitations of OneDrive.
The chapter 05 on Using SharePoint Online and OneDrive, delves into the intricacies of SharePoint Online and OneDrive, two pivotal tools within the Microsoft 365 suite. The chapter begins by discussing the functionalities of team and communication sites in SharePoint, emphasizing the organization of storage contents and the secure sharing capabilities of OneDrive for Business. It also touches upon the integration of personal and work OneDrive accounts, Information Rights Management (IRM), and the restrictions and limitations of OneDrive.
The chapter further elaborates on designing SharePoint Online sites, using SharePoint web parts, lists, document libraries, and Power Automate workflows. It underscores the importance of aligning SharePoint settings and configurations with collaboration requirements. The secure file-sharing capabilities of OneDrive for Business with Microsoft Teams colleagues are also explored.
A significant portion of the chapter is dedicated to helping Jane Doe, a fictional character, understand the nuances of SharePoint sites. Through this, readers are introduced to the potential of SharePoint Online as more than just a document storage solution.
The platform can serve as a centralized hub for academic collaboration, with robust permission settings ensuring data security. The integration of SharePoint with Microsoft Teams can also facilitate virtual classrooms, making it especially relevant in the current era of hybrid learning.
The chapter also provides an overview of SharePoint Online’s architecture, emphasizing its hierarchical object model. This model, consisting of Tenants, Farms, Site collections, and individual Sites, ensures optimal content organization and collaboration. The chapter concludes by assisting Jane in creating a SharePoint site, highlighting the various web parts and functionalities that can be incorporated.
Furthermore, the chapter touches upon the concept of Hub sites in SharePoint, which serve as central building blocks in designing and sharing content on the Intranet. These Hub sites help organize sites based on various criteria, making relevant content easily accessible.
Throughout the chapter, practical examples are provided, assisting users like Jane Doe in understanding the capabilities of SharePoint Online and OneDrive. By the end, readers are equipped with the knowledge to leverage these tools effectively, ensuring seamless collaboration and efficient data management within their organizations.
Insights:
- Seamless Integration: The integration of OneDrive with various Microsoft 365 products ensures a cohesive file-sharing experience, emphasizing the interconnectedness of the Microsoft ecosystem.
- Dynamic Platform: SharePoint Online is not just a storage solution; it’s a dynamic platform that can revolutionize content management and collaboration.
- Customization and Control: SharePoint offers a high degree of customization, allowing organizations to design sites that reflect their ethos. Moreover, it provides granular control over content sharing, ensuring data security and integrity.
Chapter 06 on Power Fx - Power Up Your Creativity: Embark on Your Journey with Microsoft Power Fx
Learn Excel-style low-code programming and delve into various facets of Power Fx. Understand functional programming to develop solutions on the Power Platform and integrate them with Microsoft Teams. This includes grasping concepts like expression grammar, imperative logic, data types, operations, variables, and tables.
Power Fx stands as a pivotal component of Microsoft’s Power Platform, offering users the ability to harness the simplicity of Excel-style formulas in a low-code programming environment. Designed to be both intuitive and powerful, Power Fx draws upon functional programming principles, allowing developers to craft robust solutions that can be seamlessly integrated with platforms like Microsoft Teams. Key to this is a deep understanding of various elements such as expression grammar, imperative logic, data types, and more.
Power Fx: The Heartbeat of Power Platform’s Low-Code Revolution Power Fx is Microsoft’s low-code formula language, primarily used within the Power Platform. Drawing inspiration from Microsoft Excel, Power Fx provides a user-friendly approach to app development, allowing both seasoned developers and business users to create solutions without the need for extensive coding.
Core Features:
- Excel-inspired Syntax: Power Fx’s syntax is reminiscent of Excel formulas, making it intuitive for users familiar with spreadsheet functions. This design choice lowers the entry barrier for many users, enabling them to leverage their existing knowledge.
- Functional Programming: At its core, Power Fx is based on functional programming principles. This means it emphasizes the use of pure functions, avoiding shared state and mutable data. This approach makes apps more predictable and easier to debug.
- Rich Set of Functions: Power Fx boasts a set of functions, covering everything from basic arithmetic operations to more complex tasks like data manipulation and string operations.
- Strongly Typed: Power Fx is a strongly typed language, ensuring that data types (like numbers, text, or records) are explicitly defined and used correctly, reducing runtime errors.
- Declarative Logic: Instead of instructing “how” to achieve something (imperative logic), Power Fx focuses on “what” you want to achieve (declarative logic). This makes the code more readable and straightforward.
Integration with Power Platform:
- Power Apps: Power Fx serves as the foundational formula language for canvas apps in Power Apps. Users can define app behavior, data manipulation, and UI interactions using Power Fx formulas.
- Extensibility: While Power Fx is primarily associated with Power Apps, Microsoft envisions it as a universal language across the Power Platform. This means we can expect its integration into other tools like Power Automate and Power Virtual Agents in the future.
Power Fx represents Microsoft’s vision for democratizing app development. By offering a language that combines the simplicity of Excel with the power of functional programming, Power Fx empowers a broader audience to participate in the app development process, bridging the gap between IT professionals and business users. As the Power Platform continues to evolve, Power Fx will undoubtedly play a central role in shaping the future of low-code application development.
Dive into the world of low-code programming with Power Fx, reminiscent of the familiar Excel environment. This dynamic language offers a deep dive into the realms of functional programming, encompassing elements like expression grammar, imperative logic, and a plethora of data types, operations, variables, and tables. Moreover, the practical application of Power Fx formulas within Power Apps further amplifies its versatility and utility. In essence, Power Fx stands as a testament to the evolving landscape of low-code development, bridging the gap between simplicity and functionality.
In conclusion, Power Fx offers a transformative approach to low-code programming, mirroring the familiarity of Excel. By delving deep into the nuances of functional programming and harnessing the capabilities of Fx formulas in Power Apps, users can unlock a new realm of efficiency and innovation in application development.
Chapter 07 on Adaptive Cards - Design, Connect, and Engage: Embark on Your Journey with Adaptive Cards
Learn the different categories of cards, including universal cards and card actions. Learn to employ Microsoft Graph and construct adaptive cards along with their task modules to address specific issues within Teams.
Adaptive Cards are a versatile way to present rich, interactive content across various platforms and applications. Designed with an open framework, these cards allow developers to create a single user interface (UI) that can be rendered consistently across multiple apps and services, such as Microsoft Teams, Outlook, and Windows Notifications. The content of an Adaptive Card is described using a JSON format, ensuring flexibility and customization. This means that, based on the platform or service, the card can adapt its appearance and functionality to provide the best user experience. Whether it’s collecting feedback through a survey, displaying dynamic content updates, or facilitating complex workflows, Adaptive Cards streamline user interactions, making them more engaging and intuitive. Their platform-agnostic nature ensures a consistent and seamless experience, regardless of where they are being viewed.
Adaptive Cards: Revolutionizing User Interactions in Modern Applications Adaptive Cards are a modern UI framework that allows developers to create interactive and rich content that can be rendered consistently across various platforms and applications. In the context of Microsoft 365, Teams, and Power Platform, Adaptive Cards play a pivotal role in enhancing user interactions and streamlining workflows.
Adaptive Cards in Microsoft 365:
- Outlook Actionable Messages: Adaptive Cards can be integrated into Outlook emails as actionable messages. This allows users to interact with the content directly from their email, such as approving a request, filling out a survey, or updating a CRM entry without leaving the Outlook interface.
- SharePoint Integration: Adaptive Cards can be used within SharePoint lists and libraries, enabling dynamic content display and user interactions directly from SharePoint sites.
Adaptive Cards in Microsoft Teams:
- Bots and Conversations: Within Teams, Adaptive Cards can be used to enhance bot interactions. For instance, a bot can send an Adaptive Card to collect user input or display search results in a structured format.
- Task Modules: These are modal pop-ups in Teams. Adaptive Cards can be used within task modules to gather detailed input from users or display rich information.
- Meeting Extensions: Adaptive Cards can be integrated into Teams meetings, allowing participants to interact with content during the meeting, such as polls or feedback forms.
Adaptive Cards in Power Platform:
- Power Automate: Adaptive Cards can be used as part of Power Automate flows. For example, a flow can be set up to send an Adaptive Card to a Teams channel when a new item is added to a SharePoint list.
- Power Apps: While Power Apps has its UI framework, developers can integrate Adaptive Cards to display data or collect input in specific scenarios, especially when consistency across multiple platforms is desired.
- Power Virtual Agents: Adaptive Cards can enhance chatbot interactions in Power Virtual Agents, allowing for richer dialogues and more structured data collection.
Designing and Templating: Adaptive Cards are described using a JSON format, making them highly customizable. The Adaptive Card Designer, available online, offers a visual interface for creating and previewing cards. Additionally, the templating feature allows for dynamic content to be injected into cards, ensuring they can be reused in various contexts with different data sets.
Discover the various types of Adaptive Cards, encompassing universal cards and their specific actions. Dive into the utilization of Microsoft Graph and the crafting of adaptive cards, combined with task modules, to tackle challenges within Teams.
Get acquainted with the range of Adaptive Cards and their corresponding actions.
Explore card design, display, adaptive card generation, and template usage.
Grasp the synergy between adaptive cards and Microsoft Graph. Uncover methods to embed adaptive cards within the Bot Framework. Comprehend the role of adaptive cards in enhancing Outlook actionable messages.
Adaptive Cards are transforming the way users interact with content across Microsoft 365, Teams, and Power Platform. By offering a consistent and interactive UI framework, they bridge the gap between various services and platforms, ensuring users have a seamless and engaging experience. As Microsoft continues to invest in this technology, it’s evident that Adaptive Cards will play an even more significant role in the future of collaborative work and business processes.
Chapter 08 on Power Apps and Dataverse - Empower Your Apps: Power Apps and Dataverse
Grasp the concepts of canvas and model-driven apps, and learn how to integrate these apps into personal apps and tab apps. Dive into the functionalities of Dataverse for Teams, its application within Teams, and recognize its limitations.
Power Apps, a key component of Microsoft’s Power Platform, is a suite that allows users to build custom applications tailored to their business needs without the necessity of extensive coding knowledge. It provides a user-friendly interface where apps can be designed to work across desktops, tablets, and mobile devices. Complementing Power Apps is Dataverse, formerly known as the Common Data Service. Dataverse is a secure and scalable data platform integrated into Power Apps, which allows users to store and manage data used by business applications. It offers a set of capabilities that include rich business data types, logic, validation, and more. Together, Power Apps and Dataverse empower businesses to create data-driven applications efficiently, ensuring that data remains integrated, current, and easily accessible across the organization. Power Apps and Dataverse: Pillars of the Power Platform Power Apps: Power Apps is a pivotal service within Microsoft’s Power Platform, designed to democratize the app development process. It provides a low-code environment, enabling both developers and business users to create custom applications tailored to their specific needs without requiring extensive coding expertise.
There are primarily three types of apps that can be created using Power Apps:
- Canvas Apps: These apps are designed from a blank canvas, much like designing a PowerPoint slide. Users can drag and drop various controls, media, and data sources onto the canvas to design the app’s user interface. The primary advantage of Canvas Apps is the flexibility they offer in terms of design and user experience.
- Model-driven Apps: These apps are data-first and are driven by the underlying data model and business processes in Dataverse. The app’s design is largely determined by the components you add and the data you choose to display. They are especially useful for complex business scenarios where the data structure and relationships are paramount.
- Portal Apps: These are external-facing apps that allow external users to view and interact with data stored in Dataverse.
Dataverse: Dataverse, previously known as the Common Data Service (CDS), is the data platform service in the Power Platform. It provides a secure and scalable environment to store and manage data used by business applications.
Key Features of Dataverse:
- Rich Data Types: Dataverse supports a wide variety of data types, from simple text and numbers to more complex types like images, files, and even custom types defined by users.
- Business Logic: Users can define business rules, workflows, and business process flows to ensure data consistency and automate processes.
- Security: Dataverse offers a robust security model, allowing administrators to define fine-grained permissions on data, ensuring that only authorized users can access or modify it.
- Integration: Dataverse is deeply integrated with the broader Microsoft ecosystem, including Power Apps, Power Automate, and Power BI. This ensures that data can flow seamlessly between different services, enabling rich and interactive applications.
- Dataverse for Teams: This is a subset of Dataverse capabilities tailored for Microsoft Teams. It allows users to build apps, flows, and chatbots directly within Teams, leveraging the power of Dataverse.
Understand the intricacies of both canvas and model-driven apps, and discover how to seamlessly incorporate them into personal and tab applications. Delve deeper into the features of Dataverse for Teams, its integration within the Teams environment, and be aware of its constraints.
Understand key elements of Microsoft Poweer Platform Dive into the design and implementation of Canvas and model-driven apps within Power Apps.
Engage with the capabilities of Dataverse for Teams, gaining insights into primary and advanced data classifications, storage alternatives (relational and non-relational), support for files and visuals, and methods for data retrieval, filtering, sorting, and advanced querying.
Evaluate the differences and similarities between Dataverse for Teams and Microsoft Dataverse to ascertain the optimal choice for integration with Microsoft 365 and Teams.
In conclusion, Power Apps and Dataverse, as integral components of the Power Platform, empower organizations to build custom solutions rapidly. While Power Apps provides the tools to design these solutions, Dataverse ensures that they are backed by a robust, secure, and scalable data platform. Together, they form the backbone of Microsoft’s vision for modern business solutions.
Chapter 09 on Security, Compliance and Licensing - Unlocking Confidence: Navigating Security, Compliance, and Licensing in Microsoft 365
Grasp the fundamentals of Cloud Security 101 and discover how to establish role-based security and identity solutions within Microsoft 365. Delve into the concepts of shared responsibility, data sovereignty, and privacy. Explore the range of Microsoft 365 plans, compare their features, and determine the most suitable option for specific situations.
In today’s digital age, understanding the intricacies of cloud security is paramount. The foundational principles of Cloud Security 101 offer insights into the challenges and potential risks that come with cloud-based solutions. Microsoft 365, a leader in this domain, emphasizes role-based security and identity solutions, ensuring that data and processes are safeguarded. A significant aspect of this is the shared responsibility model, which delineates the duties of both the cloud provider and the user. Furthermore, with increasing concerns about data sovereignty and privacy,
Microsoft 365 ensures compliance with global standards. For organizations and individuals looking to leverage Microsoft 365, a plethora of plans are available. By comparing their features, users can pinpoint the plan that aligns best with their specific needs and scenarios.
Security, Compliance, and Licensing on Microsoft 365, Teams, and Power Platform
Security:
- Microsoft 365: Microsoft 365 offers a suite of security features designed to protect user data and ensure secure communication. Features like Advanced Threat Protection (ATP), Safe Links, and Safe Attachments protect users from malicious threats. Multi-Factor Authentication MFA adds an additional layer of security, ensuring that user identities are verified before granting access.
- Teams: Microsoft Teams, as a part of the Microsoft 365 suite, inherits its robust security framework. Teams data is encrypted both in transit and at rest. Additionally, Teams complies with a range of global standards and regulations, ensuring data privacy and protection.
- Power Platform: Power Platform, which includes Power Apps, Power Automate, and Power BI, ensures data protection through its Microsoft Dataverse. Dataverse uses role-based security, field-level security, and entity-based security to protect data and ensure it’s accessed only by authorized personnel.
Compliance:
- Microsoft 365: Microsoft 365 is compliant with global standards, including GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001. The Compliance Center in Microsoft 365 provides tools to assess and manage compliance risks, conduct assessments, and implement data loss prevention (DLP) policies.
- Teams: Teams offers features like eDiscovery and Legal Hold, ensuring that organizations can meet their legal and regulatory obligations. Teams also supports compliance with industry-specific regulations, making it suitable for sectors like healthcare and finance.
- Power Platform: Power Platform adheres to the same compliance standards as Microsoft 365. It offers tools for auditing and monitoring activities, ensuring that apps and flows meet organizational and regulatory compliance requirements.
Licensing:
- Microsoft 365: Licensing for Microsoft 365 varies based on organizational needs. There are different plans tailored for businesses, educational institutions, and individual users. Each plan offers a different set of tools and features, allowing organizations to choose based on their specific requirements.
- Teams: While Teams is included in most Microsoft 365 subscriptions, there are also standalone plans available. Organizations can choose from various licensing options based on the features they need, such as audio conferencing or phone system capabilities.
- Power Platform: Licensing for Power Platform is modular. Organizations can license individual components like Power Apps, Power Automate, or Power BI separately. There are also dedicated plans for more intensive users or developers, ensuring flexibility and scalability.
Understanding Cloud Security in the Microsoft 365 Ecosystem Dive deep into the core principles of Cloud Security 101 and recognize the potential vulnerabilities and threats inherent to cloud platforms. Understand the pivotal elements that constitute a robust cloud security framework, ensuring its resilient deployment. Microsoft 365 stands out by offering a suite of security and compliance tools tailored to meet diverse needs. By evaluating the myriad of Microsoft 365 subscription plans, users can select the one that best resonates with their requirements, be it for individual use, SMEs, or large corporations.
In conclusion, Microsoft 365, Teams, and Power Platform provide a holistic approach to security, compliance, and licensing. Their integrated tools and features ensure that organizations can operate securely, meet regulatory standards, and choose licensing options that align with their needs.
Chapter 10 on AI Builder - Building Intelligence: AI Builder on the Power Platform
Learn the concept of prebuilt AI models, such as the business reader, category classification, and entity extractor, to augment the real-time business solutions discussed in the preceding chapter.
AI Builder, integrated within the Power Platform, offers a suite of prebuilt AI models designed to enhance business solutions. These models, including the business reader, category classification, and entity extractor, provide users with the capability to automate processes, gain insights, and make predictions based on their data. By leveraging these models, businesses can streamline operations, make informed decisions, and create more efficient workflows. The Power Platform’s AI Builder is especially beneficial for those looking to harness the power of AI without the need for extensive coding or data science expertise.
Leverage the AI Builder on the Power Platform to utilize pre-configured AI models. Acquaint yourself with the pre-established models, content structuring, understanding documents, and content-related services. Dive into real-world examples and hands-on applications within the Power Platform.
AI Builder on Power Platform: An Overview
The Power Platform by Microsoft has always been about empowering users to create solutions that streamline business processes, and with the introduction of AI Builder, this capability has been significantly enhanced. AI Builder is a turnkey solution that allows even those without a background in data science to harness the power of artificial intelligence (AI) in their applications.
- What is AI Builder? AI Builder is an AI-enhanced data platform integrated within the Power Platform. It provides a user-friendly interface that allows users to build, train, and deploy machine learning models without writing a single line of code. This no-code approach democratizes AI, making it accessible to a broader range of users.
- Prebuilt AI Models: One of the standout features of AI Builder is its collection of prebuilt AI models. These models cater to common business scenarios and can be easily integrated into Power Apps and Power Automate. Some of the notable prebuilt models include:
- Business Reader: Extracts information from documents, receipts, and invoices.
- Category Classification: Categorizes text based on predefined categories.
- Entity Extractor: Identifies and extracts specific data points from text, such as dates, names, or product details.
- Custom Models: Beyond the prebuilt models, AI Builder offers tools for users to build and train custom models tailored to their specific needs. This involves using your data to teach the model and then refining it until it achieves the desired accuracy.
- Integration with Power Platform: The true strength of AI Builder lies in its seamless integration with other Power Platform components. For instance:
In Power Apps, users can create applications that utilize AI to enhance user experience, from image recognition to sentiment analysis.
With Power Automate, AI Builder can automate processes that involve data processing, anomaly detection, or predictive analysis.
- Data Connectivity: AI Builder is designed to work harmoniously with Microsoft’s data platform, Dataverse, ensuring that data used for model training is easily accessible, consistent, and secure.
- Licensing and Pricing: While AI Builder comes with its own licensing model, it’s structured to be cost-effective, especially for businesses that are already invested in the Microsoft ecosystem. The pricing varies based on the number of runs and the type of models used.
AI Builder on the Power Platform represents a significant stride in the democratization of AI. By providing tools that are both powerful and user-friendly, Microsoft ensures that businesses of all sizes can leverage AI to innovate, optimize processes, and deliver value. Whether you’re looking to automate document processing, gain insights from data, or enhance your apps with AI-driven features, AI Builder offers a toolkit to achieve those goals.
Concluding chapter 11 on Generative AI and LLM based apps- Unleash Creativity: Exploring Generative AI, LLM-based Apps, and Beyond
This chapter delves into Generative AI and LLMs-based applications, guiding citizen developers or business users on understanding the nuances of Generative AI and LLMs. This knowledge will empower them to integrate AI into their business’s digital framework. Generative AI and Large Language Models (LLMs) have become buzzwords in the tech industry, but their implications and applications, especially for citizen developers and business users, are profound. This chapter aims to demystify these concepts and provide actionable insights for their practical application in business scenarios.
- Introduction to Generative AI: Generative AI refers to a subset of artificial intelligence that focuses on creating new content. It can generate text, images, music, and more by training on vast datasets. The generated content can often be indistinguishable from that created by humans, making it a powerful tool for various applications, from content creation to problem-solving.
- Large Language Models (LLMs): LLMs, like OpenAI’s GPT series, are a type of Generative AI specifically designed for text generation. They are trained on vast amounts of text data, enabling them to produce coherent and contextually relevant passages. Their capabilities range from answering questions and writing essays to coding and more.
- Empowerment through Knowledge: For citizen developers or business users, understanding Generative AI and LLMs is not just about grasping the underlying technology. It’s about recognizing the potential these tools offer for enhancing business processes, improving customer interactions, and driving innovation. By integrating AI into their digital framework, businesses can automate tasks, generate insights, and offer enhanced user experiences.
- Third-Party Power Platform Connectors: The Power Platform’s versatility is further enhanced by a plethora of third-party connectors available in the marketplace. These connectors allow for the integration of LLMs-based apps, enabling businesses to harness the power of models like OpenAI’s GPT-3 directly within their applications.
- Utilizing OpenAI APIs in Power Apps: One of the practical applications of LLMs in the Power Platform is the integration of OpenAI APIs into Power Apps. Through Power Automate flow, businesses can automate processes that leverage the capabilities of these AI models, from answering customer queries to generating content on the fly.
- Emerging Trends in Citizen Development: The landscape of citizen development is rapidly evolving, with AI playing a pivotal role. Tools like AI Builder offer no-code AI solutions, while OpenAI provides powerful text generation capabilities. Microsoft’s Co-pilot, on the other hand, assists developers by suggesting code snippets in real-time. These tools, among others, are shaping the future of citizen development, making it more accessible, powerful, and AI-driven.
Review this book on Goodreads https://go.amitpuri.com/gr-cd-m365

Unlock an exciting opportunity to dive into a captivating read at an unbeatable price! If you’re in the US, visit https://go.citizendeveloper.codes/kindle-cd-m365-us to take advantage of the Kindle Countdown Deal. For those in the UK, your special offer awaits at https://go.citizendeveloper.codes/kindle-cd-m365-uk. Don’t miss out on this limited-time offer to enrich your library with this must-read book. Act now and be part of an enthralling reading experience!
Enjoy reading and reimagine the world around you!


Work in progress
Based on the article from Microsoft’s Work Trend Index, here are the key bullet points about Copilot’s impact on generative AI at work:
- Productivity and Time Savings:
- 70% of Copilot users reported increased productivity.
- Users were 29% faster in tasks like searching, writing, and summarizing.
- 64% found Copilot helpful in spending less time processing emails.
- 85% said Copilot aids in achieving a good first draft faster.
- 75% noted that Copilot saves time by finding needed information in files.
- Quality and Creativity Improvement:
- 68% of users observed an improvement in the quality of their work.
- 57% felt more creative using Copilot.
- Copilot was found to help in jump-starting the creative process and generating ideas while writing.
- User Preference and Dependence:
- 77% of users expressed that they wouldn’t want to work without Copilot after using it.
- A significant number of users preferred having access to Copilot over free lunches at work.
- 30% said access to Copilot would influence their choice of employer.
- Specific Use Cases:
- In a study, Copilot users summarized a missed meeting nearly 4 times faster than those without it.
- Emails written with Copilot were rated as more clear and concise.
- Copilot reduced the effort needed to complete tasks, with 85% of users acknowledging this benefit.
These points highlight Copilot’s significant role in enhancing productivity, creativity, and efficiency in the workplace, with users showing a strong preference for its continued use.
Read more What Can Copilot’s Earliest Users Teach Us About Generative AI at Work?
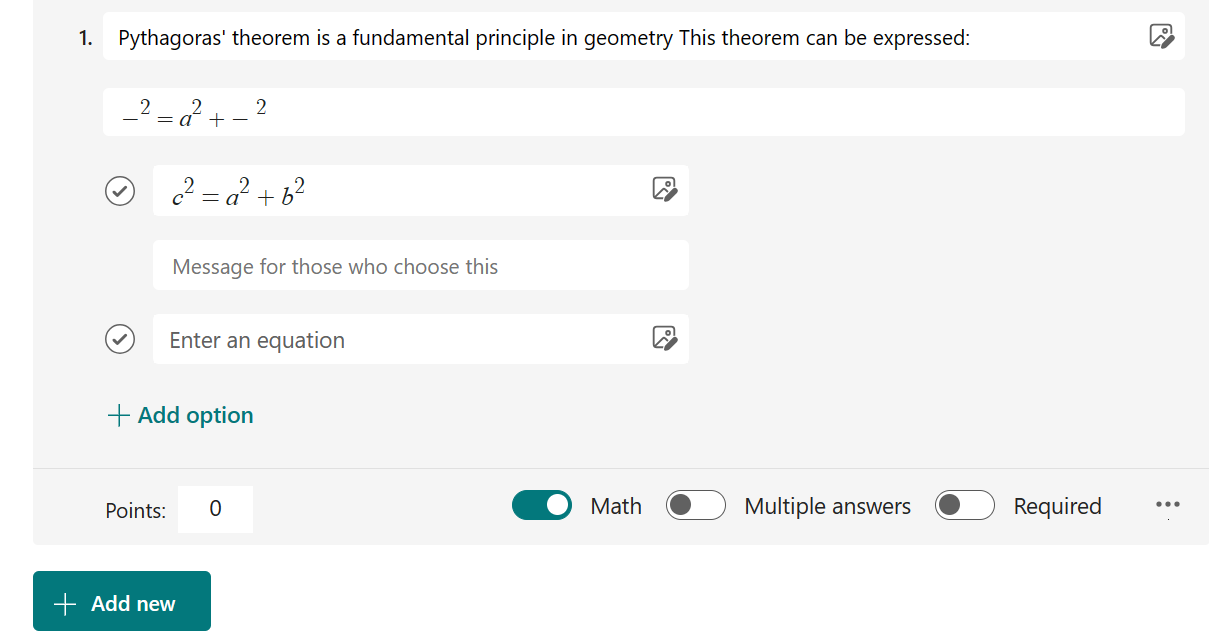
Recent enhancements in Microsoft Forms aid teachers in time management, more effective student interaction, and trend analysis.
The recent updates to Microsoft Forms, as detailed in the Microsoft EDU blog, offer several enhancements for educational assessments:
-
Forms App Updates: Enables the creation of quizzes, surveys, and forms directly within the app, streamlining the process compared to the previous necessity of using the Forms website.
-
Efficient Quiz Creation: Automates quiz development by allowing educators to upload existing documents (Word, PDFs) which Forms converts into online quizzes, saving significant time in question development and formatting.
-
Enhanced Assessment Management: Offers advanced control features for assessments, such as setting timers, sending reminders, shuffling question order, and allowing students to save and edit their responses.
-
Engagement Through Polls in Teams: Integrates the use of polls in Microsoft Teams meetings, enhancing interactivity and student engagement during synchronous lessons.
-
Sharing and Presentation Features: Facilitates sharing quizzes and forms with a broader audience, including young students and guardians, through methods like QR codes and embedding in learning management systems. The new Present mode in Forms allows for live, interactive feedback collection and display.
-
Insights Feature for Analysis: Forms now includes an Insights feature that analyzes and highlights trends in student responses, providing actionable information. It also allows exporting data to Microsoft Excel for further analysis.
These updates aim to transform assessment methods in education, making the process more efficient, interactive, and insightful for educators and students.
Read more on Transform assessment with new Forms updates
The SharePoint Roadmap Update for Fall 2023, as presented at the Microsoft 365 Conference in May 2023, details several key enhancements and themes for SharePoint:
-
Simplified Authoring: Improvements in SharePoint’s authoring experience include the introduction of Copilot in SharePoint, which integrates LLMs and Microsoft Graph for content creation. Features include simplified canvas actions, private drafts, an advanced image editor, and a new site template experience for easier page and site creation.
-
Compelling Content: Enhancements focus on aesthetic capabilities, allowing more sophisticated and engaging page designs. The new Brand Center helps specify organizational branding elements, and Microsoft Stream and Clipchamp integration facilitate video content creation and sharing.
-
Deeper Engagement: SharePoint integrates with Viva Amplify for more effective internal communication and engagement. New capabilities include centralized campaign management and multi-channel publishing. Additionally, SharePoint News in Outlook and multiple Viva Connections experiences cater to diverse employee needs.
-
Flexible Platform: The SharePoint Framework (SPFx) updates enhance custom business process integration. New features include SPFx updates for Viva Connections card layout options, the SharePoint Web UI toolkit for design customization, and improved third-party cookie handling.
These updates aim to make SharePoint a more intuitive, engaging, and flexible platform, enhancing the ability to create and manage content effectively within organizations.
Read more on SharePoint Roadmap Update – Fall 2023





Comments